Request an online quote today.
 All Uploads are Secure and Confidential
All Uploads are Secure and ConfidentialCertifications:
ISO 13485 | IATF 16949

Nylon PA 12
Metal Powders
Composite Materials
Standard Resins
Tough Resins
Flexible Resins
Castable Resins
Nylon PA 12
TPU
PLA
ABS
PETG
Nylon
Properties: Known for its strength and durability.
Properties: Good for general-purpose applications.
Properties: Enhanced properties for specific engineering applications.
Properties: Good for general-purpose applications.
Properties: Designed for functional parts requiring durability.
Properties: Suitable for applications needing elasticity.
Properties: Ideal for jewelry and dental applications.
Properties: Known for its strength and flexibility.
Properties: A flexible material ideal for applications requiring elasticity.
Properties: Biodegradable and easy to print, ideal for prototypes.
Properties: Strong and heat-resistant, suitable for functional parts.
Properties: Combines strength and flexibility, perfect for mechanical components.
Properties: Durable and flexible, great for end-use parts.

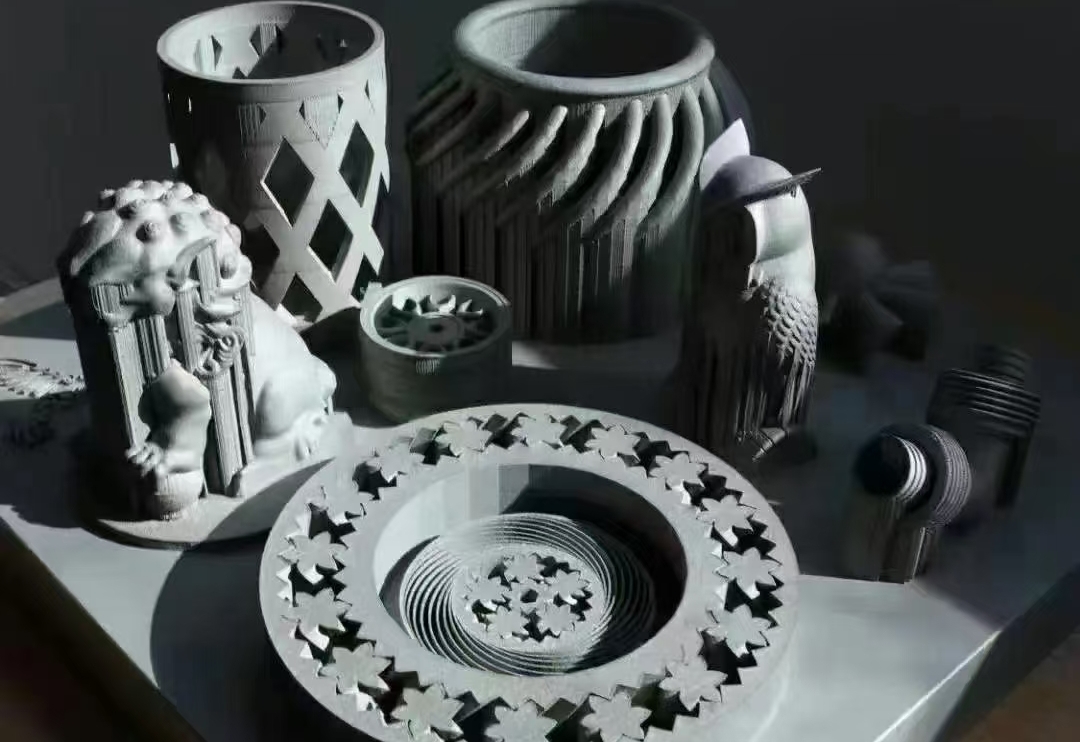
304
303
420
430
316
Properties: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, good thermal and electrical conductivity.
Applications: Aerospace components, automotive parts, structural frames, heat exchangers.
Benefits: Excellent machinability, high strength-to-weight ratio, and availability in various alloys fortailored applications.
Properties: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, good thermal and electrical conductivity.
Applications: Aerospace components, automotive parts, structural frames, heat exchangers.
Benefits: Excellent machinability, high strength-to-weight ratio, and availability in various alloys fortailored applications.
Properties: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, good thermal and electrical conductivity.
Applications: Aerospace components, automotive parts, structural frames, heat exchangers.
Benefits: Excellent machinability, high strength-to-weight ratio, and availability in various alloys fortailored applications.
Properties: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, good thermal and electrical conductivity.
Applications: Aerospace components, automotive parts, structural frames, heat exchangers.
Benefits: Excellent machinability, high strength-to-weight ratio, and availability in various alloys fortailored applications.
Properties: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, good thermal and electrical conductivity.
Applications: Aerospace components, automotive parts, structural frames, heat exchangers.
Benefits: Excellent machinability, high strength-to-weight ratio, and availability in various alloys fortailored applications.

6063
6061
Properties: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, good thermal and electrical conductivity.
Applications: Aerospace components, automotive parts, structural frames, heat exchangers.
Benefits: Excellent machinability, high strength-to-weight ratio, and availability in various alloys fortailored applications.
Properties: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, good thermal and electrical conductivity.
Applications: Aerospace components, automotive parts, structural frames, heat exchangers.
Benefits: Excellent machinability, high strength-to-weight ratio, and availability in various alloys fortailored applications.

Grade 2
Grade 4
Grade 5
Properties: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, good thermal and electrical conductivity.
Applications: Aerospace components, automotive parts, structural frames, heat exchangers.
Benefits: Excellent machinability, high strength-to-weight ratio, and availability in various alloys fortailored applications.
Properties: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, good thermal and electrical conductivity.
Applications: Aerospace components, automotive parts, structural frames, heat exchangers.
Benefits: Excellent machinability, high strength-to-weight ratio, and availability in various alloys fortailored applications.
Properties: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, good thermal and electrical conductivity.
Applications: Aerospace components, automotive parts, structural frames, heat exchangers.
Benefits: Excellent machinability, high strength-to-weight ratio, and availability in various alloys fortailored applications.

H59
H62
Properties: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, good thermal and electrical conductivity.
Applications: Aerospace components, automotive parts, structural frames, heat exchangers.
Benefits: Excellent machinability, high strength-to-weight ratio, and availability in various alloys fortailored applications.
Properties: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, good thermal and electrical conductivity.
Applications: Aerospace components, automotive parts, structural frames, heat exchangers.
Benefits: Excellent machinability, high strength-to-weight ratio, and availability in various alloys fortailored applications.

T1
T2
T3
C11000
C12200
Properties: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, good thermal and electrical conductivity.
Applications: Aerospace components, automotive parts, structural frames, heat exchangers.
Benefits: Excellent machinability, high strength-to-weight ratio, and availability in various alloys fortailored applications.
Properties: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, good thermal and electrical conductivity.
Applications: Aerospace components, automotive parts, structural frames, heat exchangers.
Benefits: Excellent machinability, high strength-to-weight ratio, and availability in various alloys fortailored applications.
Properties: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, good thermal and electrical conductivity.
Applications: Aerospace components, automotive parts, structural frames, heat exchangers.
Benefits: Excellent machinability, high strength-to-weight ratio, and availability in various alloys fortailored applications.
Properties: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, good thermal and electrical conductivity.
Applications: Aerospace components, automotive parts, structural frames, heat exchangers.
Benefits: Excellent machinability, high strength-to-weight ratio, and availability in various alloys fortailored applications.
Properties: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, good thermal and electrical conductivity.
Applications: Aerospace components, automotive parts, structural frames, heat exchangers.
Benefits: Excellent machinability, high strength-to-weight ratio, and availability in various alloys fortailored applications.

Fe 360 A
Fe 430 A
Properties: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, good thermal and electrical conductivity.
Applications: Aerospace components, automotive parts, structural frames, heat exchangers.
Benefits: Excellent machinability, high strength-to-weight ratio, and availability in various alloys fortailored applications.
Properties: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, good thermal and electrical conductivity.
Applications: Aerospace components, automotive parts, structural frames, heat exchangers.
Benefits: Excellent machinability, high strength-to-weight ratio, and availability in various alloys fortailored applications.

GCr6
GCr9
GCr15
Properties: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, good thermal and electrical conductivity.
Applications: Aerospace components, automotive parts, structural frames, heat exchangers.
Benefits: Excellent machinability, high strength-to-weight ratio, and availability in various alloys fortailored applications.
Properties: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, good thermal and electrical conductivity.
Applications: Aerospace components, automotive parts, structural frames, heat exchangers.
Benefits: Excellent machinability, high strength-to-weight ratio, and availability in various alloys fortailored applications.
Properties: Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, good thermal and electrical conductivity.
Applications: Aerospace components, automotive parts, structural frames, heat exchangers.
Benefits: Excellent machinability, high strength-to-weight ratio, and availability in various alloys fortailored applications.

| Feature | SLS | FDM | SLA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Types | Nylon, Plastics | ABS, PLA, TPU | Photopolymer Resin |
| Precision | High | Medium | Extremely High |
| Application | Functional Parts | Prototyping | High Detail Models |
| Lead Time | Medium | Fast | Medium |

 What is 3D Printing?
What is 3D Printing?
3D printing is a technology that manufactures objects by stacking materials layer by layer, also known as additive manufacturing. It starts from digital design files (such as STL format) and uses various materials (like plastics, metals, resins, etc.) to print complex shapes and structures that traditional methods cannot easily achieve.
 What materials can be used in 3D printing?
What materials can be used in 3D printing?
Common 3D printing materials include:
The choice of material typically depends on the application requirements, durability, cost, and processing precision of the printed item.
 What are the differences between 3D printing and traditional manufacturing methods?
What are the differences between 3D printing and traditional manufacturing methods?
Unlike traditional manufacturing methods (such as casting, cutting, molding, etc.), 3D printing is an additive manufacturing process that constructs objects by layering materials without the need for molds or machining tools. This method can produce very complex structures while reducing waste and processing time. Additionally, 3D printing allows for personalized customization, making it ideal for small batch production and prototype design.
 How to ensure the quality of 3D printed models?
How to ensure the quality of 3D printed models?
Key factors for ensuring 3D printing quality include:
 What is the precision of 3D printing?
What is the precision of 3D printing?
The precision of 3D printing depends on various factors, including the type of printer used, materials, and printing settings. Generally, FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) printers have a precision range of 0.1mm to 0.5mm, while SLA (Stereolithography) printers can achieve a precision of around 0.05mm.
 What applications are suitable for 3D printing?
What applications are suitable for 3D printing?
3D printing is widely applied in multiple fields, including:
As technology advances, the range of applications for 3D printing continues to expand.
 What is the cost of 3D printing?
What is the cost of 3D printing?
The cost of 3D printing varies due to several factors, including:
Generally, 3D printing is suitable for small batch production or personalized customization; for large-scale production, traditional manufacturing methods may be more cost-effective.
 How to choose the appropriate 3D printing technology?
How to choose the appropriate 3D printing technology?
Choosing the right 3D printing technology requires consideration of several factors: