Request an online quote today.
 All Uploads are Secure and Confidential
All Uploads are Secure and ConfidentialCertifications:
ISO 13485 | IATF 16949
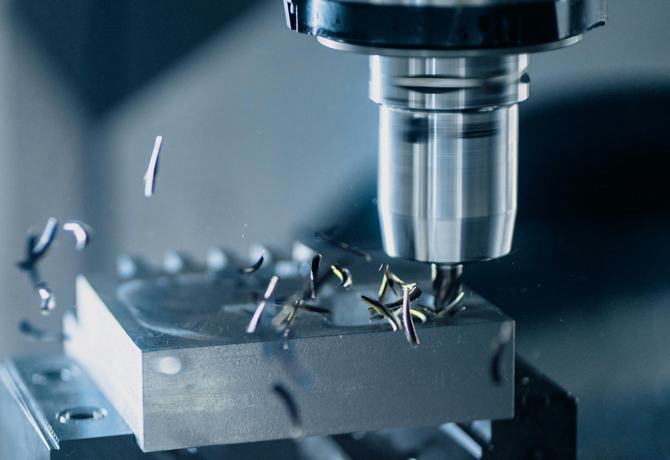


6061
6063
Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, good thermal and electrical conductivity.
Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, good thermal and electrical conductivity.

316
430
420
303
304
High strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and heat resistance.
High strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and heat resistance.
High strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and heat resistance.
High strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and heat resistance.
High strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and heat resistance.

H62
H59
Good machinability, corrosion resistance, and antimicrobial properties.
Good machinability, corrosion resistance, and antimicrobial properties.

C12200
C11000
T3
T2
T1
High electrical and thermal conductivity, ductility, and corrosion resistance.
High electrical and thermal conductivity, ductility, and corrosion resistance.
High electrical and thermal conductivity, ductility, and corrosion resistance.
High electrical and thermal conductivity, ductility, and corrosion resistance.
High electrical and thermal conductivity, ductility, and corrosion resistance.

Grade 5
Grade 4
Grade 2
High strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility.
High strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility.
High strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility.

Fe 430 A
Fe 360 A
High tensile strength, hardness, and wear resistance.
High tensile strength, hardness, and wear resistance.

GCr15
GCr9
GCr6
High hardness, wear resistance, and ability to retain sharp edges.
High hardness, wear resistance, and ability to retain sharp edges.
High hardness, wear resistance, and ability to retain sharp edges.

Polypropylene
PVC
PTFE
Polycarbonate
Delrin
PEEK
Nylon
ABS
Lightweight, good chemical resistance, and fatigue resistance.
Good chemical resistance, lightweight, and durable.
Low friction, high chemical resistance, and thermal stability.
High impact resistance, optical clarity, and good dimensional stability.
Low friction, high stiffness, and excellent dimensional stability.
High thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical strength.
High tensile strength, wear resistance, and low friction.
Lightweight, impact-resistant, and easy to machine.


 What is CNC Machining?
What is CNC Machining?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining is a technology that utilizes computers to control machine tools for processing. Through precise numerical control programs, CNC machines can produce high-precision parts from materials such as metal and plastic. This technology is widely used in various fields, from prototype production to mass manufacturing.
 How to choose materials suitable for CNC machining?
How to choose materials suitable for CNC machining?
Choosing suitable materials for CNC machining requires consideration of several factors:
 What documents are required for CNC machining?
What documents are required for CNC machining?
To ensure machining accuracy, we typically require you to provide design drawings (in CAD format) and technical specifications of the parts, including dimensions, tolerances, surface treatments, and material requirements. If your parts have special requirements, you can also provide relevant testing standards and quality requirements.
 What is the precision of CNC machining?
What is the precision of CNC machining?
Our CNC machined parts can achieve a minimum tolerance of ±0.003mm, making them highly suitable for the production of precision parts that meet most industrial standards.
 What materials can CNC machining use?
What materials can CNC machining use?
CNC machining is widely applied to the processing of various materials, including metals (such as aluminum, stainless steel, titanium alloys), plastics (such as POM, ABS, nylon), and other composite materials. Different materials will be selected for different machining methods and tools based on their characteristics.
 What is the typical lead time for CNC machining?
What is the typical lead time for CNC machining?
The lead time for CNC machining typically depends on the complexity of the parts and the quantity of the order. For small batches or single prototypes, we can deliver within a few days to a week. For large-scale production, the lead time will be extended accordingly. Specific timelines can be customized based on your needs.
 How do you ensure the quality of CNC machining?
How do you ensure the quality of CNC machining?
We ensure the precision and consistency of each part through strict quality control processes. Each machining step undergoes precise measurement and inspection to ensure the final product meets design requirements. Additionally, our team conducts detailed quality checks before and after machining to ensure each part is defect-free.
 How is the cost of CNC machining calculated?
How is the cost of CNC machining calculated?
The cost of CNC machining is typically influenced by several factors:
 Is CNC machining suitable for mass production?
Is CNC machining suitable for mass production?
CNC machining is not only suitable for producing single prototype parts but is also very well-suited for mass production. With precise numerical control systems and efficient production processes, we can maintain consistency and high precision in mass production. This makes CNC machining an ideal choice for large-scale industrial manufacturing.
 What are the advantages of CNC machining compared to traditional machining methods?
What are the advantages of CNC machining compared to traditional machining methods?
The greatest advantages of CNC machining over traditional manual machining are its high precision, efficiency, and consistency. With computer control, CNC can achieve precise machining of complex shapes and details while reducing manual operations and errors. Additionally, CNC machining can significantly improve production efficiency and shorten delivery times.